Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC), commonly known as Cellulose Gum, is a water-soluble polyanionic compound derived from cellulose through a series of processes including alkalization, etherification, neutralization, and washing. Renowned for its versatility and cost-effectiveness, CMC is the most widely produced cellulose ether globally.
As a high-performance additive, LANDERCOLL Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose is available in food, oil drilling, textile printing, batteries, and papermaking industries.
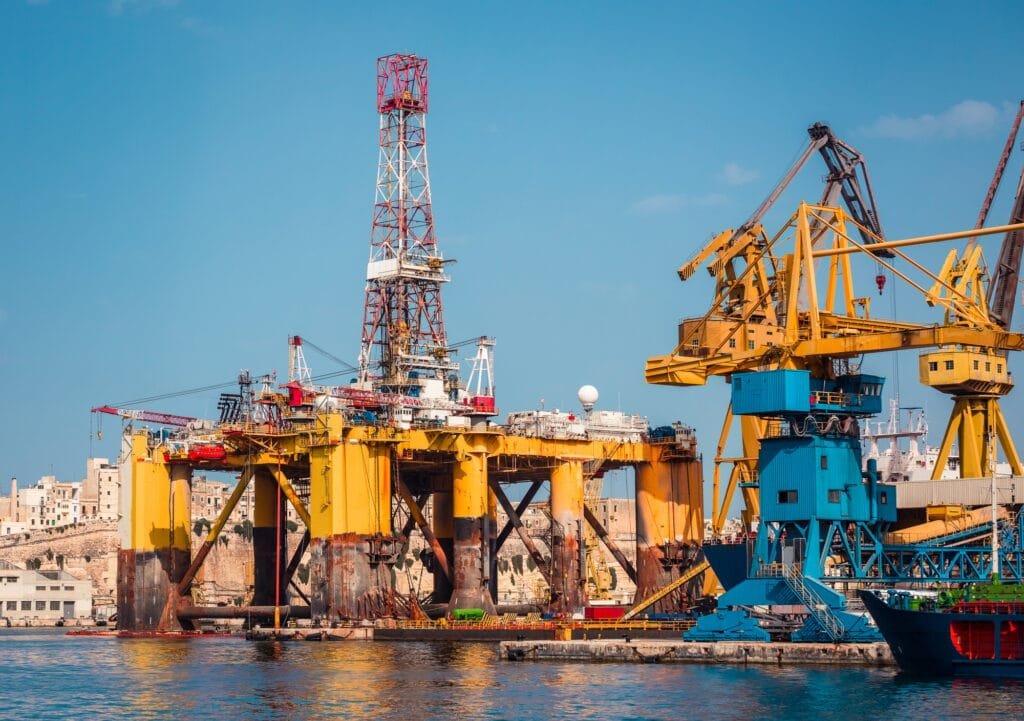
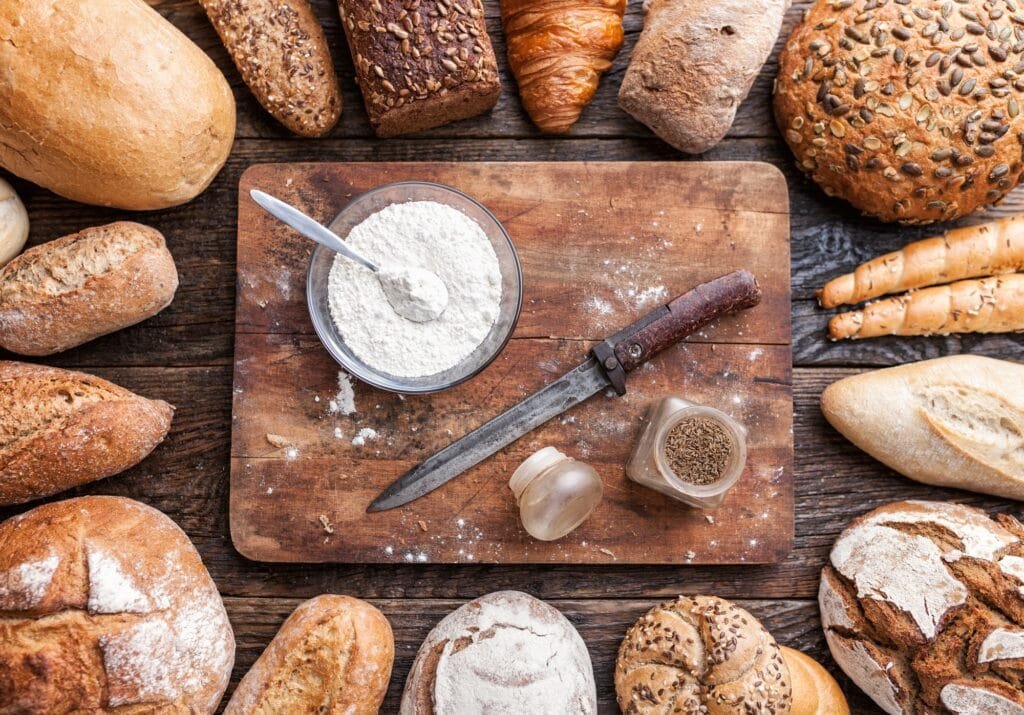
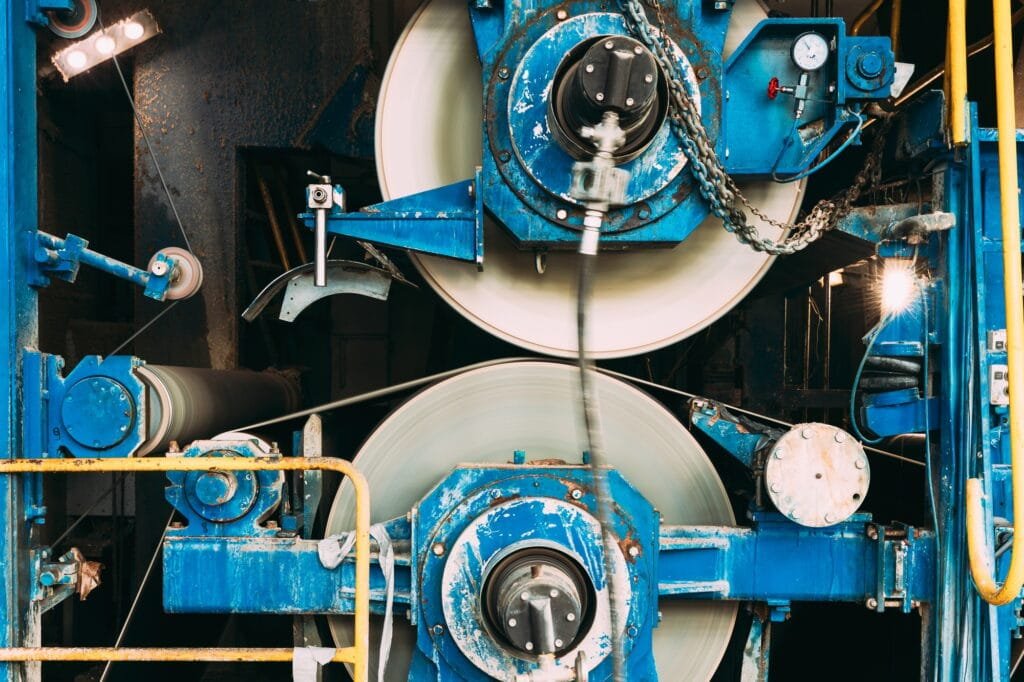





CMC exhibits excellent cold-water solubility, forming clear colloidal solutions at concentrations up to 5% w/v. Unlike HPMC or HEC, it remains stable in both acidic (pH 3-12) and high-ionic-strength environments, making it ideal for brine-based systems. Solubility decreases in organic solvents but can be enhanced via sodium salt forms.
As a GRAS (FDA 21 CFR §182.1745) ingredient, CMC serves multiple roles:
Yes. CMC (DS 0.7-1.2) provides:
However, combine with 0.1-0.3% guar gum for optimal gas retention.
Key quality metrics:
Neem vandaag nog contact op met LANDERCOLL voor gedetailleerde informatie en richtlijnen!